Open and Closed Film Insulation
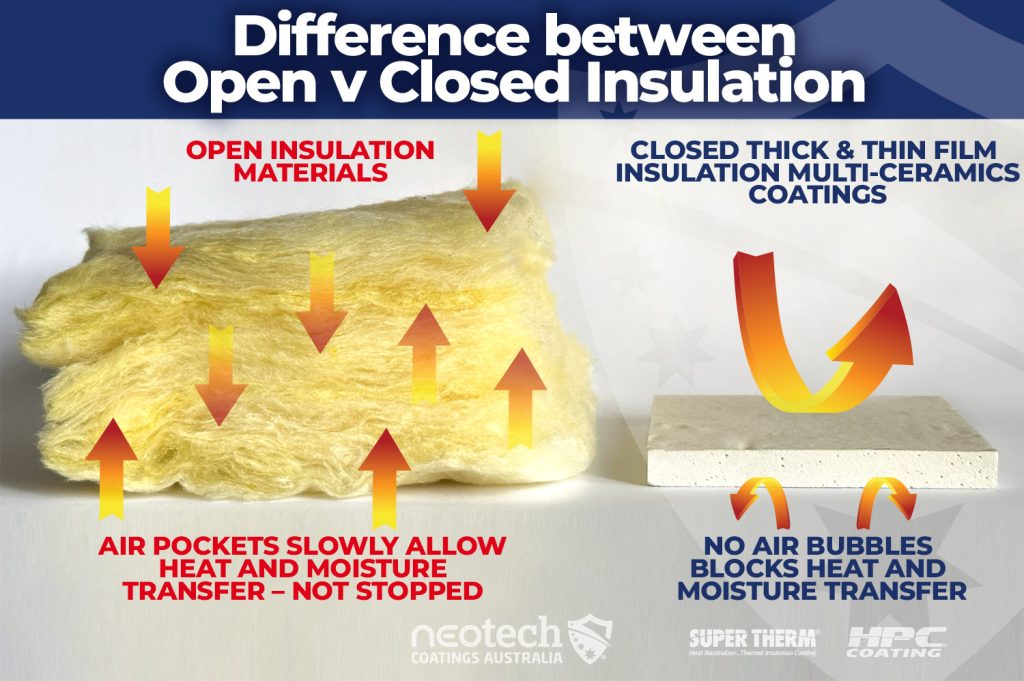
There is a BIG distinction between OPEN and CLOSED film and material insulation. Open film insulation utilises air pockets and fillers that aim to slow heat transfer; but not block the heat. Once the heat has transferred, the Open material or coating film reaches heat flux.
Closed film insulation works to block the heat on the surface and reflect heat. These closed film thermal insulation coatings help prevent moisture and air to enter the coating film which dramatically decreases CUI, gives permanent personal protection, offers long-lasting energy reduction costs, reduces CO2, provides sustainable asset performance and most of all blocks the ‘initial loading of heat’ on the surface therefore, reducing the amount of heat available to load and transfer to the cool side.
Open film uses the older insulation conductivity language of R values or heat resistance. The new realm of closed film multi-ceramics thermal insulation coatings (TIC) that block radiation heat (thin film) or block and hold conductive heat on the surface (thick film) work on permeability. The alternative new generation of multi-ceramics formula coatings provides new methods of TICs without being affected by moisture and air flow creating a closed film TIC heat block.
Closed Insulation : there’s no air fillers, blocks heat and moisture transfer
Our coatings are closed film multi-ceramics thin and thick coatings:
- Super Therm® closed thin film
- Sunshield® closed thin film
- HPC® closed thick film
- HSC® closed thick film
Open Film Insulation
- Open film as a coating, sheet or layer of material used to insulate something, like a wall, roof or pipe
- Open film insulation allows air and moisture to pass through it. It is not completely sealed, so it lets air circulate and transfer slowly
- This type of insulation is useful when you want to regulate temperature and humidity in a space while still allowing some ventilation
- Cannot offer long term personnel protection
Closed Film Insulation
- A Closed film is also a coating, sheet or layer of material used for insulation, but it’s different from open film insulation
- Closed film insulation does not allow air, heat and moisture to pass through. It forms a sealed barrier, preventing air from moving freely
- This type of insulation is great when you want to create a more airtight and controlled environment, preserving temperature and reducing the transfer of heat or cold from outside
- Able to offer safety and permanent personnel protection
The relationship between these two types of insulation is essentially about how much airflow and moisture they allow. They serve different purposes based on their properties:
- Complementary Usage: In many situations, using a combination of both open film and closed film insulation may be beneficial. For instance, you might use closed film insulation to create a well-insulated and airtight core, while strategically incorporating open material insulation in certain areas to manage allow ventilation and moisture. While it is proven moisture does decrease the efficiency of many materials and their insulation properties.
- Balance of Airflow and Insulation: The choice between open and closed film insulation depends on the specific needs of the building or space. Sometimes, you want better insulation with minimal airflow (closed film), and other times, you want insulation allowing some ventilation (open film).
- Climate and Building Type: The climate and the purpose of the building influence the choice of insulation. For example, in a humid environment, using open film insulation can help prevent moisture buildup, while in colder regions, closed film insulation might be preferred to keep the heat inside.
Open film insulation allows airflow and moisture to pass through, while closed film insulation forms an airtight barrier to better preserve temperature and reduce external influences.
Impacts of Heat Load
Heat load calculations traditionally are for figuring out the amount of heat needed to keep an enclosure within the desired temperature range (FieldVibe, 2020). If heat from internal (ie pipe) or external (ie solar) influence pushes through a material it loads fully to eventually reach a heat flux. If radiated solar heat trying to enter a structure can be reduced significantly as a closed film TIC does, it reduces the amount of heat available for transfer and, therefore, acts to control the conduction of heat and heat load and becomes a non-conductor.
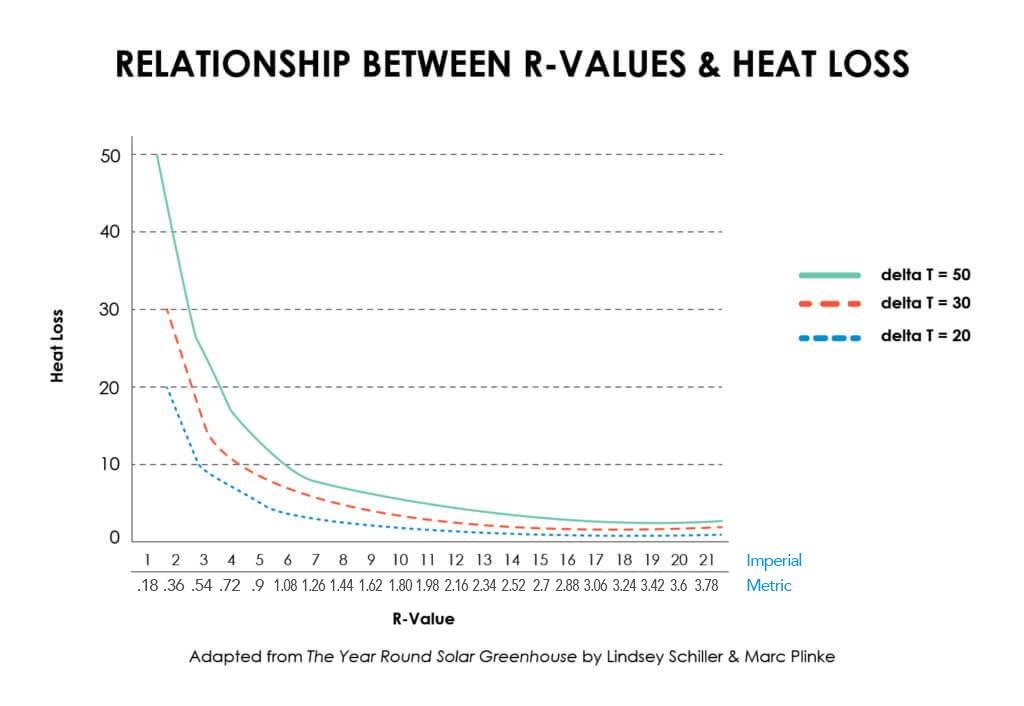
With less heat load available for transfer, there is less heat available for conduction into the asset. In a pipe situation, the majority of heat load is controlled and blocked on the initial surface, no R or K value is required for closed film ceramics TICs. Blocking the initial heat load is the ‘key’ to controlling heat transfer and flow into or out of a structure like an airflow barrier. Mainstream insulation materials or open film ‘air-filled’ materials depend solely on slowing or resisting absorbed heat for a given period of time and then allowing it through to transfer at a controlled rate. These materials aren’t designed to stop the loading and transferring heat load and therefore work on conductive measurements of R and K values.
As shown below, adding more thickness to open materials doesn’t actually slow the air, moisture and heat transfer rate. Since 1979, the idea that you only slow the absorption and resulting flow speed of heat into the insulation material, then as it fully loads (reaching heat flux), it then passes through the material to the cool side. At this point, the idea that “if it is not working good enough, put more thickness in your wall or ceiling or around your pipe or tank to buy more time before it reaches “heat flux”. Open insulation never stops the initial absorption and flow of all this heat through the material to the cool side.
These materials based on R-values were (as established by the ASTM test procedures ASTM C177 or C518) to only be tested at 23°C inside a controlled lab with no wind and little to no humidity. Was this ever real-world conditions. Our Closed film thin insulation coating, Super Therm® with the help of NASA (1989-1995), developed a ceramic insulation coating that blocks the initial heat load on the surface, preventing up to 96% of the initial heat load, thereby reducing the heat “available” for transfer down to approximately 4%.
Measurement Values
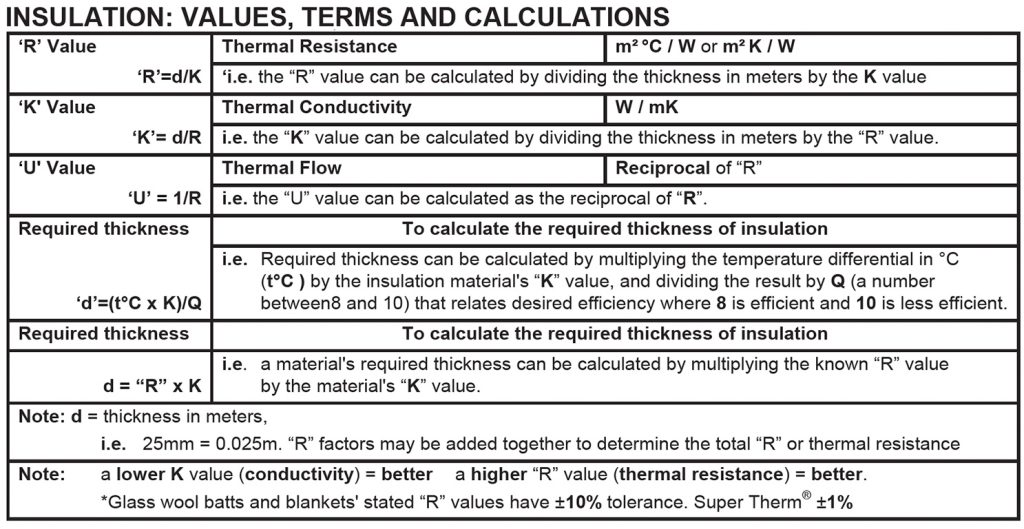
The values used to measure the effectiveness of conductive insulations are primarily related to their thermal performance and ability to resist heat transfer. These values help in comparing and selecting the most suitable insulation for specific applications. Here are some of the key measurements used:
- R-Value (Thermal Resistance) – Open:
- R-Value is a measure of thermal resistance and indicates how well an insulation material can resist heat transfer.
- The higher the R-Value, the better the insulation’s ability to prevent heat from passing through it.
- R-Value is commonly used for comparing the effectiveness of different open insulation materials. For instance, an insulation material with an R-Value of 5 is more effective than one with an R-Value of 3.
- U-Value (Thermal Conductance) – Open and Closed:
- U-Value, also known as thermal conductance, is the inverse of R-Value. It measures the rate of heat transfer through a material.
- A lower U-Value indicates better insulating properties, as it means less heat can pass through the material.
- U-Value is often used in building construction to assess the overall thermal efficiency of walls, windows, roofs, etc.
- K-Value (Thermal Conductivity) – Open:
- K-Value, or thermal conductivity, measures how well a material can conduct heat.
- Lower K-Values indicate better insulating properties, as it means the material is less conductive and will resist heat flow more effectively.
- C-Value (Thermal Capacity) – Open and Closed:
- C-Value, or thermal capacity, measures the ability of a material to store and release heat.
- Materials with high C-Values can store heat and act as thermal mass, helping to regulate temperature fluctuations.
- Perm Rating (Permeance) – Open and Closed:
- Perm rating measures the ability of an insulation material to allow moisture to pass through.
- Lower perm ratings indicate more moisture resistance, which can be important to prevent issues like mould growth.
- Air Permeability – Open:
- Air permeability measures the ease with which air can pass through an insulation material.
- In some cases, it is desirable to have some air permeability to allow controlled ventilation and prevent moisture buildup.
Thin and Thick Ceramics Thermal Coatings
How to Qualify at Thermal Insulation Coating
Super Therm – thin closed film multi-ceramics insulation
Super Therm® is considered a “thin closed film multi-ceramics insulation coating.” A high-performance water based coating designed primarily as a heat-blocking, reflect and protective coating for various surfaces, including roofs and walls.
Super Therm® is manufactured by Superior Products International II, Inc. (SPI). It is known for its ability to reflect and dissipate heat, which can help reduce the amount of heat absorbed by a building’s exterior. It is often used as an energy-efficient coating to improve thermal performance, reduce cooling costs, and enhance comfort inside the building.
Key features and benefits of Super Therm® include:
- Reflective Properties: Super Therm® is formulated with ceramics that provide exceptional reflective capabilities. It reflects a significant portion of solar radiation, reducing the heat absorbed by the coated surface. It also has other ceramics that include the correct:
- Material make up
- Crystalline structure
- Processed method
- Size
- Density
- Insulating Effect: While not a traditional insulation material, Super Therm‘s reflective properties create a “cool roof” effect by preventing the transfer of heat into the building. This can help maintain a more stable and comfortable indoor temperature.
- Weather Protection: Super Therm® is also known for its weather-resistant properties, protecting surfaces from harsh environmental conditions and extending the lifespan of the coated surfaces.
- Sustainable Benefits: By reducing the energy required for cooling, Super Therm® can contribute to lowering carbon emissions and making buildings more environmentally friendly.
Super Therm® compliments traditional insulation materials like fibreglass, foam, or mineral wool, which provide thermal resistance by slowing down the transfer of heat. Instead, it reduces the heat load on the building envelope and enhancing energy efficiency and reduces costs.
As with any building product, proper application is essential to achieving the desired performance. If you are considering using Super Therm® or any other coating for insulation purposes, it’s advisable to consult with professionals and ensure it aligns with your specific needs and requirements.
HPC – Thick closed film multi-ceramics insulation
HPC® (Hot Pipe Coating) is a ceramic based, water-borne insulating coating designed to insulate in high temperature situations from 100° to 600°C. Maximum energy efficiency with a high temperature coating designed to insulate every surface
- Replaces wraps and jacketing
- Eliminates CUI (corrosion under insulation)
- Easy to repair
- Easy to maintain
- Reduce energy
- Water based and safe application
- Protects personnel
- No shut down required
HPC® Coating provides a “true insulation benefit” by holding the heat inside of the coated vessel and increasing the internal temperature/pressure if the energy source is not changed. Energy costs can be saved by reducing the energy requirement to maintain the original temperature or the manufacturing process can be improved by increasing the internal temperature of the vessel to achieve a more efficient and effective process.









